728x90


https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2573
TASK
1. 1년에 얼만큼 녹는지 확인
2. 두 덩어리가 되는 지 보기 -> BFS
1. 하나씩 확인
입력
import sys
from collections import deque
input = sys.stdin.readline
# 행 열
n, m = map(int, input().split())
graph = []
for _ in range(n):
graph.append(list(map(int, input().split())))
direction = [(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1)]
1번 태스크를 위한 함수
def count_0(nowx, nowy):
cnt = 0
for dx, dy in direction:
x = nowx + dx
y = nowy + dy
if 0<=x<n and 0<=y<m:
if graph[x][y] == 0:
cnt += 1
return cnt상하좌우를 확인하여 0이면 cnt + 1을 한다
2번 태스크를 위한 함수
def bfs(graph, visited, nowx, nowy):
queue = deque([(nowx, nowy)])
visited[nowx][nowy] = False # 방문하면 False
while queue:
nowx, nowy = queue.popleft()
for dx, dy in direction:
x = nowx + dx
y = nowy + dy
if 0<=x<n and 0<=y<m:
if graph[x][y] != 0 and visited[x][y] == True:
queue.append((x,y))
visited[x][y] = False
덩어리가 나눠지는지 확인
result = 0 # 실제 덩어리가 두 개 이상이 될 때 반환할 값
cnt = 0 # 년도 추가
# 모두 0이 아닐 때까지(모두 녹기 전까지)
while graph != [[0]*m for _ in range(n)]:
# 얼마나 녹는지 담을 리스트
zero = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if graph[i][j] != 0:
zero[i].append(count_0(i, j))
# 녹는 것만큼 뺀다
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if graph[i][j] != 0:
graph[i][j] = graph[i][j]-zero[i][j] if graph[i][j]-zero[i][j]>0 else 0
cnt += 1 # 1년 추가
visited = [[True]*m for _ in range(n)] # 방문 리스트
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if graph[i][j] == 0: # 바다는 False, 빙하는 True
visited[i][j] = False
res = 0 # 덩어리
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if visited[i][j]: # 빙하면
bfs(graph, visited, i,j)
res += 1 # 덩어리 추가
# print(i, j)
# 두 덩어리 이상이면
if res > 1:
result = cnt
break
print(result)
문제점: 두 번의 for문을 반복해서 돌기 때문에 python으로 실행했을 때 시간 초과
-> pypy를 사용
2. 최적화하기
for문을 없애고 최적화하기 위해
바다(0)가 아닌 빙하가 있는 위치 인덱스를 key로 한 딕셔너리를 만들고 value에 상하좌우 cnt 0을 넣었습니다.
그리고 이 딕셔너리를 for문으로 반복했씁니다.
입력(위와 동일)
import sys
from collections import deque
input = sys.stdin.readline
# 행 열
n, m = map(int, input().split())
graph = []
for _ in range(n):
graph.append(list(map(int, input().split())))
direction = [(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1)]
1번 태스크를 위한 함수(위와 동일)
def count_0(nowx, nowy):
cnt = 0
for dx, dy in direction:
x = nowx + dx
y = nowy + dy
if 0<=x<n and 0<=y<m:
if graph[x][y] == 0:
cnt += 1
return cnt
2번 태스크를 위한 함수
def bfs(graph, visited, nowx, nowy):
queue = deque([(nowx, nowy)])
visited[nowx][nowy] = False # 방문하면 False
while queue:
nowx, nowy = queue.popleft()
for dx, dy in direction:
x = nowx + dx
y = nowy + dy
if 0<=x<n and 0<=y<m:
if graph[x][y] != 0 and visited[x][y] == True:
queue.append((x,y))
visited[x][y] = False
key가 위치 인덱스이고, value가 count 0 값인 딕셔너리 nonzero
0이 아닌 빙하들 값만 저장
nonzero = {}
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if graph[i][j] != 0:
nonzero[(i,j)] = count_0(i,j)
덩어리가 나눠지는지 확인
for i in range(n) for j in range(m) 대신
for i, j in nonzero
result = 0
cnt = 0
while graph != [[0]*m for _ in range(n)]:
# 좌표와 빙산이 - 되는 걸 같이 적는 리스트
for x, y in nonzero:
graph[x][y] = max(0, graph[x][y] - nonzero[(x,y)])
for x, y in nonzero:
if graph[x][y] != 0:
nonzero[(x,y)] = count_0(x,y) # 다시 업데이트
cnt += 1
visited = [[True]*m for _ in range(n)]
res = 0
for i, j in nonzero:
if visited[i][j]==True and graph[i][j]!=0:
bfs(graph, visited, i,j)
res += 1
# print(i, j)
if res > 1:
result = cnt
break
print(result)
결과
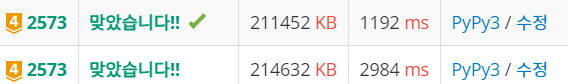
물론 2번은 파이썬으로도 통과가 되었습니다

필요없는 부분은 돌지 않도록 반복문을 잘 설정해야겠다는 생각을 했습니다